Hypertension - causes, complications, treatment and more
Hypertension is a prevalent and often silent health condition that affects 1.28 billion adults aged 30-79 years old. In Singapore 1 in 3 adults aged 18 and 74 adults have high blood pressure.
What is hypertension?
Hypertension is blood pressure more than 140/90 mm Hg in patients who do not have pre-existing conditions in Singapore.
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, occurs when the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high. It’s a leading cause of various serious health complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems. While the American Heart Association (AHA) has defined hypertension as blood pressure more than 130/80 mm Hg, Ministry of Health (Singapore) has not changed the definition of hypertension as of yet. Our local guidelines state hypertension as blood pressure more than 140/90 mm Hg in patients who do not have other pre-existing conditions.
| Normal | High Normal | High | |
| Systolic BP (mm Hg) | 100-130 | 130-139 | > 140 |
| Diastolic BP (mm Hg) | 60-85 | 85-89 | >90 |
In patients who have existing conditions of chronic kidney disease, and diabetes, it is recommended for them to keep their blood pressure within 120/80 mmHg.
For patients who develop high blood pressure during pregnancy, it is important that they continue regular follow-ups with their obstetrician as high blood pressure in a pregnant lady may indicate pre-eclampsia.
What is Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure?
To comprehend hypertension, it’s essential to grasp the basics of blood pressure. Blood pressure readings consist of two numbers: systolic blood pressure (the higher number) represents the force when the heart beats, and diastolic blood pressure (the lower number) represents the heart’s resting phase.
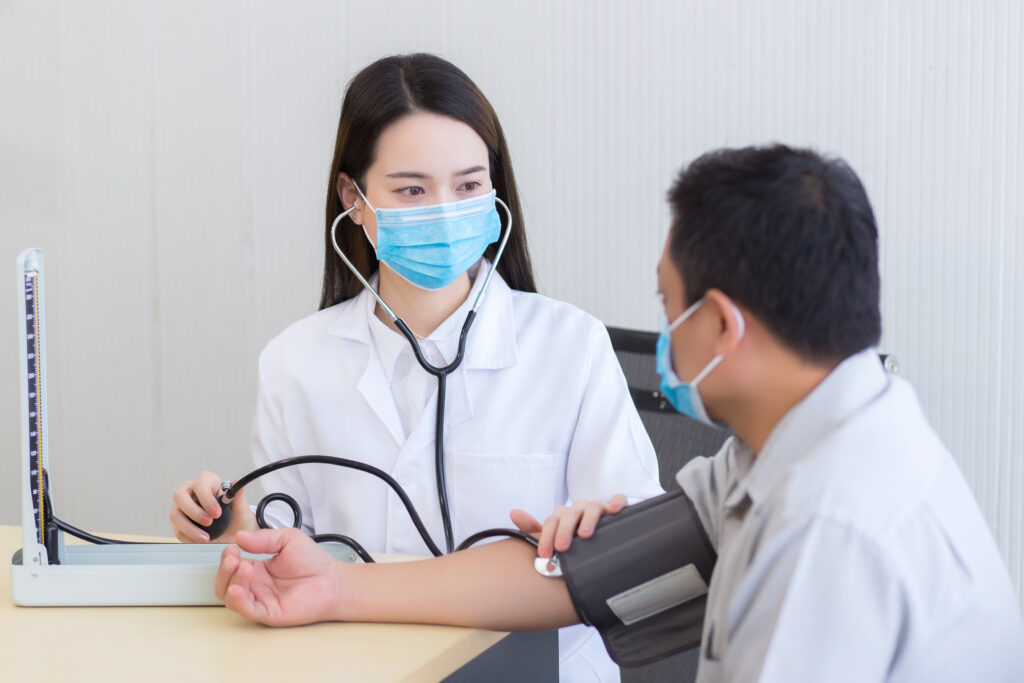
Measuring Blood Pressure
To determine if one is hypertensive, it is best to visit your family doctor for a blood pressure measurement. Your doctor should use the sphygmomanometer to wrap around your upper arm to determine if you have hypertension. Usually an elevated blood pressure reading does not immediately confirm the diagnosis of hypertension as it requires at least two elevated blood pressure readings on two separate days before the diagnosis of hypertension is made.
Causes and Risk Factors of High Blood Pressure
In the following section, we will discuss the risk factors of higher blood pressure reading:
Lifestyle Influences
- Dietary Habits: High sodium intake, excessive alcohol consumption, and a diet rich in processed foods can increase blood pressure.
- Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles increase the risk of hypertension. Regular exercise promotes heart health and aids in blood pressure regulation.
- Smoking: Tobacco use adversely affect blood vessels, leading to hypertension. Besides, smoking is also detrimental to the heart. Smokers are two to four times more likely to get heart attack than non-smokers
Genetic and Medical Factors
- Family History: Genetic predisposition plays a role; if your first degree family member has a history of hypertension, you might be at higher risk of developing high blood pressure.
- Underlying Conditions: Chronic kidney disease, hormonal imbalances, and sleep disorders can contribute to hypertension.
Sometimes, there may be secondary causes of hypertension. These may include the following:
- Kidney disease
- Side effects of medications such as steroids
- Obstructive sleep apnea
Detecting Hypertension
Symptoms and Diagnosis of High Blood Pressure
Hypertension is often asymptomatic, earning its title as the “silent killer.” Occasionally, hypertension may present with headaches, giddiness, blurring of vision or nose bleeds. Regular blood pressure measurements are crucial to determine if one is truly hypertensive. In Singapore, the health screening program, Screen for Life, screens normal healthy person for hypertension every 3 years.
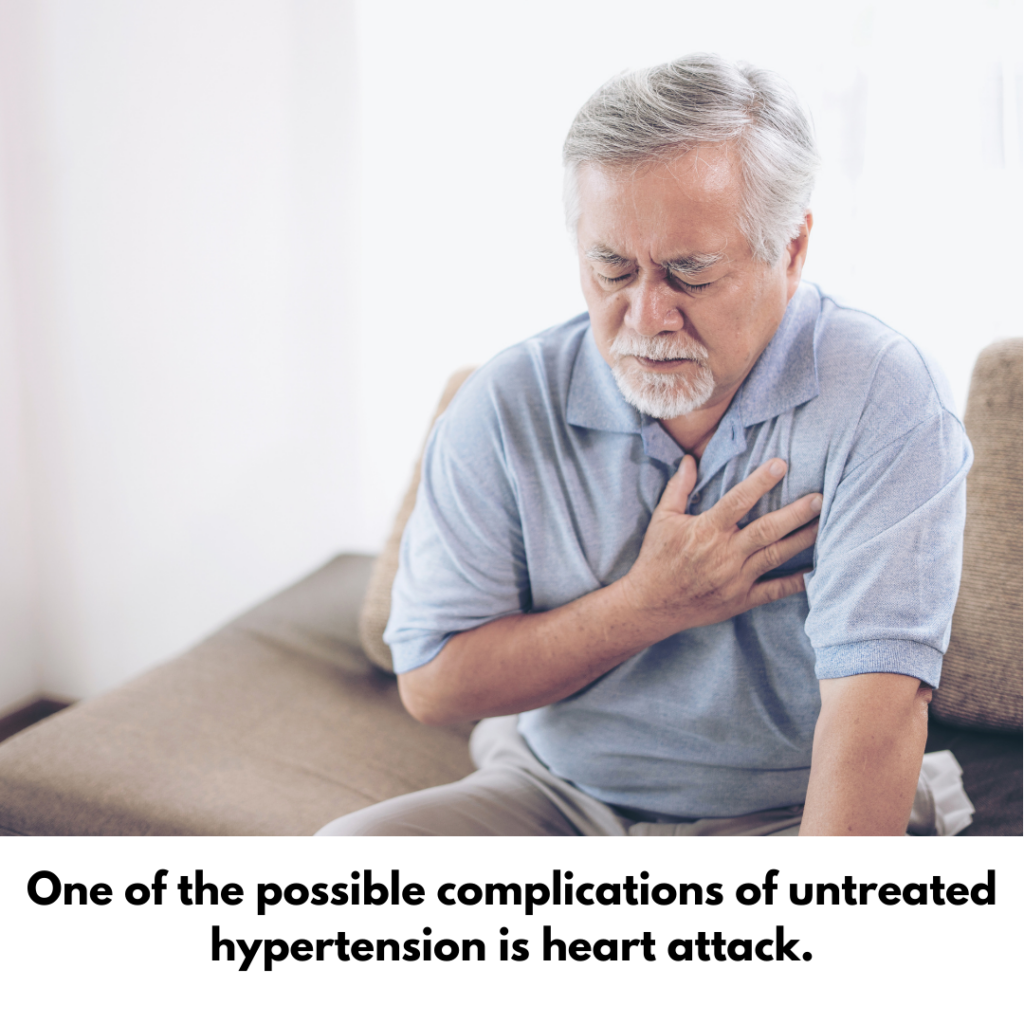
Complications
Untreated hypertensive complications include heart attacks, cardiac failure, strokes, kidney problems, and vision impairment. Heart attacks typically present as chest pain. Prolonged high blood pressure causes enlargement of the heart muscle which may result in cardiac failure. Heart failure patients typically present with breathlessness on normal activities of living such as walking.
The risk of stroke also increases with high blood pressure. When the blood vessels supplying the brain undergo prolonged elevated force stretching and dilating the vessel walls, the blood vessel becomes weaker and more easily rupture resulting in a stroke or otherwise known as cerebrovascular disease or cerebrovascular events.
Lifestyle Modifications to Prevent High Blood Pressure
As a first step, hypertensive patients are strongly encouraged to make lifestyle modifications to treat their hypertension and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Dietary Approaches for Patients with Hypertension
– DASH Diet: The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, legumes, and low-fat dairy while limiting snacks, sweets, and meats. Studies show significant lower blood pressure with this approach.
– Sodium Reduction: Lowering sodium intake complements the DASH diet, further aiding in blood pressure control. In our culture, common sources of high salt content contributing to increased blood pressure readings include gravy, bone stock soup, soya sauce, oyster sauce, processed food such as ham.
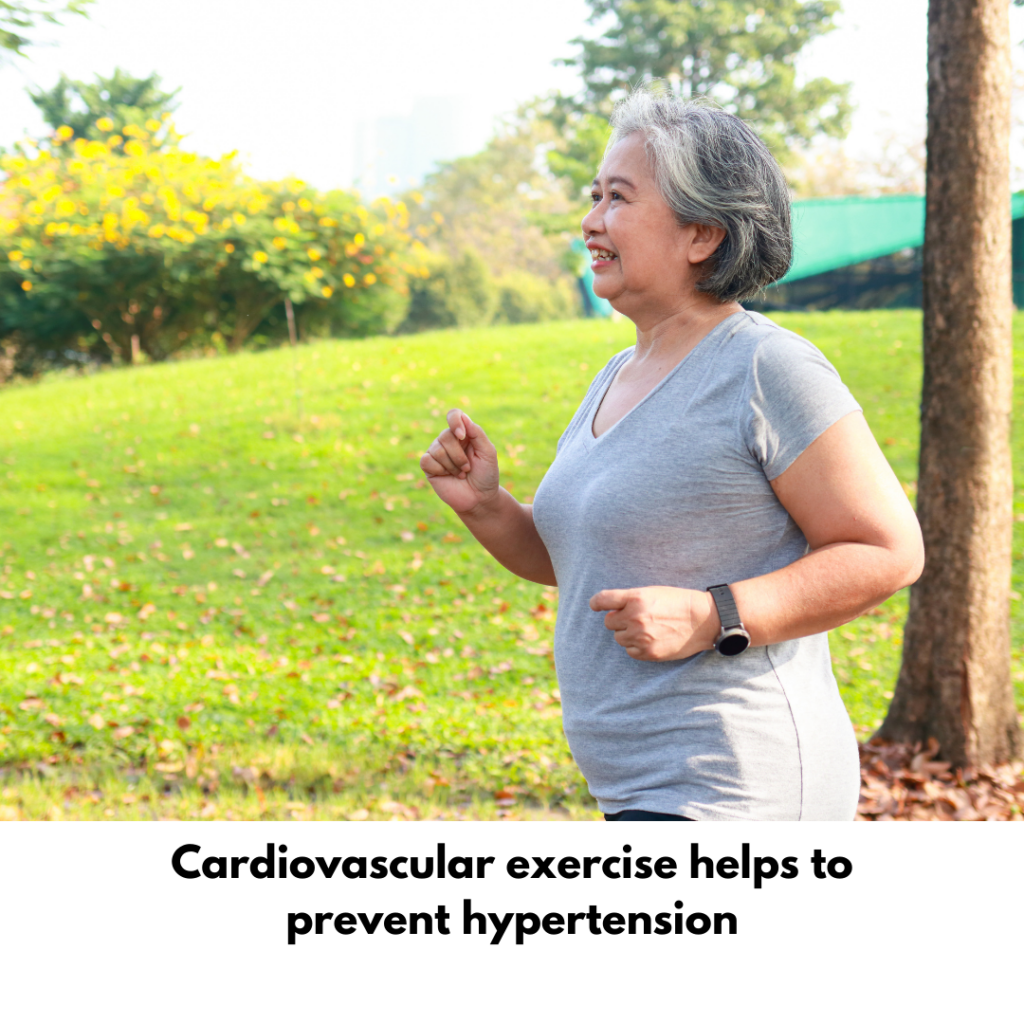
Physical Activity
– Cardiovascular Exercise: Aerobic activities like jogging, and swimming enhance cardiovascular health, helping in blood pressure regulation and prevent high blood pressure. Typically activities that increase the heart rate is considered beneficial for high blood pressure. One should aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate intensity aerobic exercises on most day of the week as this will improve the health of one’s heart.
Hypertensive Medications to Lower Blood Pressure
Antihypertensive Medications
Various treatments are useful in managing blood pressure. These include ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics, and calcium channel blockers. Each group of medicine come with its own side effects, therefore consultation with a doctor is essential for proper medication management. For instance, ACE-inhibitors may cause high potassium levels in the blood.
Combination Therapies
In some cases, combination medicine involving different types of treatment might be necessary to achieve optimal blood pressure control. Regular follow-ups and having your blood pressure and medications reviewed are crucial. It is also important to bring your home blood pressure reading so that your doctor can determine if the readings are elevated.
Patients who are diagnosed with hypertension usually undergo further blood tests to ensure that their kidney function has not been affected by high blood pressure. If their kidney function has indeed been compromised, the blood tests will also help to tell us if the patient which stage of chronic kidney disease the patient is in. These services are usually easily accessible at a regular family clinic
Hypertension Myths and Facts
Myth: Only the Elderly Get Hypertension
Reality: Hypertension can affect people of all ages, including young adults and even children. Regular screenings are vital regardless of age.
Myth: Stress Alone Causes Hypertension
Reality: While stress can temporarily elevate blood pressure, it’s not the sole cause. Genetics, lifestyle, and overall health contribute significantly.
Summary: Hypertension / High blood pressure
As we conclude this comprehensive guide on hypertension, remember that knowledge and proactive lifestyle changes are your best allies against this condition. By adopting a heart-healthy diet, staying physically active and adhering to medical advice, you can lead a life free from high blood pressure.
Consult your family doctors for personalized guidance, and together, let’s conquer hypertension and embrace a healthier future.
Disclaimer: No content on this site should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Are hypertension medications blood thinners?
No, hypertension medications are not blood thinners
Are hypertension and diabetes related?
As the risk factors for hypertension and diabetes are rather similar – an unhealthy diet, sedantary lifestyle, it is no surprise that some patients have both hypertension and diabetes. However, this does not mean that if one is diagnosed with hypertension, he/she will have diabetes.
Can hypertension be cured?
While hypertension cannot be cured, it can be controlled by lifestyle modications, and medications.
How do you reduce hypertension?
Lifestyle modifications such as a low-sodium DASH diet, regular cardiovascular physical exercise can help to reduce hypertension.